프로그래밍/자료구조 && 알고리즘
[Java] 배열(Array)
코드몬스터
2022. 9. 27. 19:50
728x90
★ 본 내용은 "코드잇의 자바 객체지향 프로그래밍" 및 " 김영한의 자바 입문" 을 듣고 정리한 내용입니다. ★
배열이란?
- 같은 타입의 여러 변수를 하나의 묶음으로 다루는 것
- 참조변수(score)를 통해서 배열을 관리
- 연속적으로 붙어있다.
- 크기를 변경할 수 없는 정적 배열이다.
int[] score = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}배열 선언 및 생성
- 배열을 선언하고 생성을 해야만 메모리 공간(저장)이 할당된다.
int[] score; // 1. 배열 score를 선언(참조변수)
score = new int[5]; // 2. 배열의 생성(int 저장공간)
int[] score = new int[5]; // 3. 배열 선언과 생성을 동시
배열 초기화
- 배열의 각 요소에 처음으로 값을 저장하는 것
- ⭐ 배열을 선언과 생성만 하고 초기화하지 않고 출력하는 경우 0 으로 채워져 있다.
int[] score = new int[5];
int[] score = new int[]{50, 60, 70, 80} // 1번 방법
int[] score = {50, 60, 70, 80}; // 2번 방법, 거의 2번 방법을 사용
// 에러 발생
int[] score;
score = {50, 60, 70, 80};
배열 출력
- Arrays.toString 을 사용해서 모두 출력 가능
- for 반복문을 사용해서 배열의 요소를 하나씩 출력 가능
import java.util.Arrays; // Arrays 클래스
int[] iArr = {100, 95, 80, 70, 60}
// output: [100, 95, 80, 70, 60]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(iArr));
char[] chArr = {'a', 'b', 'c', 'd'};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(chArr));
// for문 출력 방법1
for(int i = 0; i < iArr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(iArr[i]);
}
// for문 출력 방법2
for (int num: iArr) {
System.out.println(num);
}
// ⭐ 초기화 하지 않고 선언만 하고 출력하는 경우
int[] test = new int[5];
// output: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(test));
배열 인덱스
- 배열 메모리 주소의 각 요소에 붙는 번호

배열 길이
- 배열은 한 번 생성하면 실행 동안 그 길이를 바꿀 수 없다.
int tmp = arr.length; // arr.length의 값은 5이고 tmp에 5가 저장
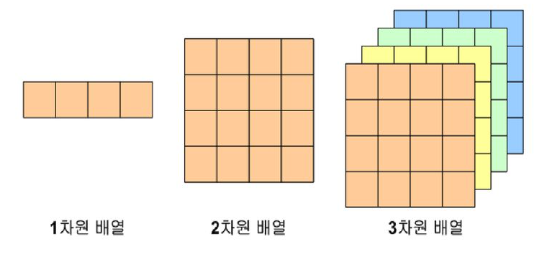
다차원 배열
요소의 길이가 같은 2차원 배열

- 예시
int[][] arr = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6}
}; // 2차원 배열 // 생성과 초기화 동시에
요소의 길이가 다른 2차원 배열
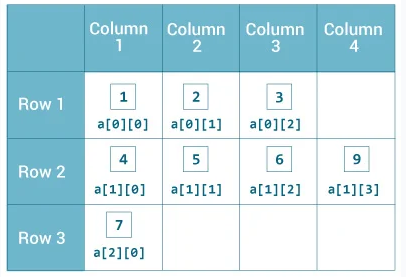
- 예시
class MultidimensionalArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a 2d array
int[][] a = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6, 9},
{7},
};
// calculate the length of each row
System.out.println("Length of row 1: " + a[0].length);
System.out.println("Length of row 2: " + a[1].length);
System.out.println("Length of row 3: " + a[2].length);
// Print all elements of 2d array Using Loop
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < a[i].length; ++j) {
System.out.println(a[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
3차원 배열
- 2차원 배열을 요소로 가지고 있다.
- 2차원 배열과 같이 길이를 표시할 수 있다.
- 예시
class ThreeArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a 3d array
int[][][] test = {
{
{1, -2, 3},
{2, 3, 4}
},
{
{-4, -5, 6, 9},
{1},
{2, 3}
}
};
// for..each loop to iterate through elements of 3d array
for (int[][] array2D: test) {
for (int[] array1D: array2D) {
for(int item: array1D) {
System.out.println(item);
}
}
}
}
}
참고 사이트